
The main difference between metaphase 1 and 2 is that chromosomes are attached as homologous pairs at the equator during the metaphase 1 and during metaphase 2, single chromosomes are attached at the equator. During prophase, they separate to provide. This organelle controls the microtubules in the cell, and each centriole is one half of the organelle. Prophase, in both mitosis and meiosis, is recognized by the condensing of chromosomes and separation of the centrioles in the centrosome.

Homologous chromosomes can exchange parts in a process called "crossing over. How is metaphase 1 and 2 different Metaphase 1 is associated with meiosis 1 whereas the metaphase 2 is associated with meiosis 2. Prophase is the starting stage of cell division in eukaryotes.
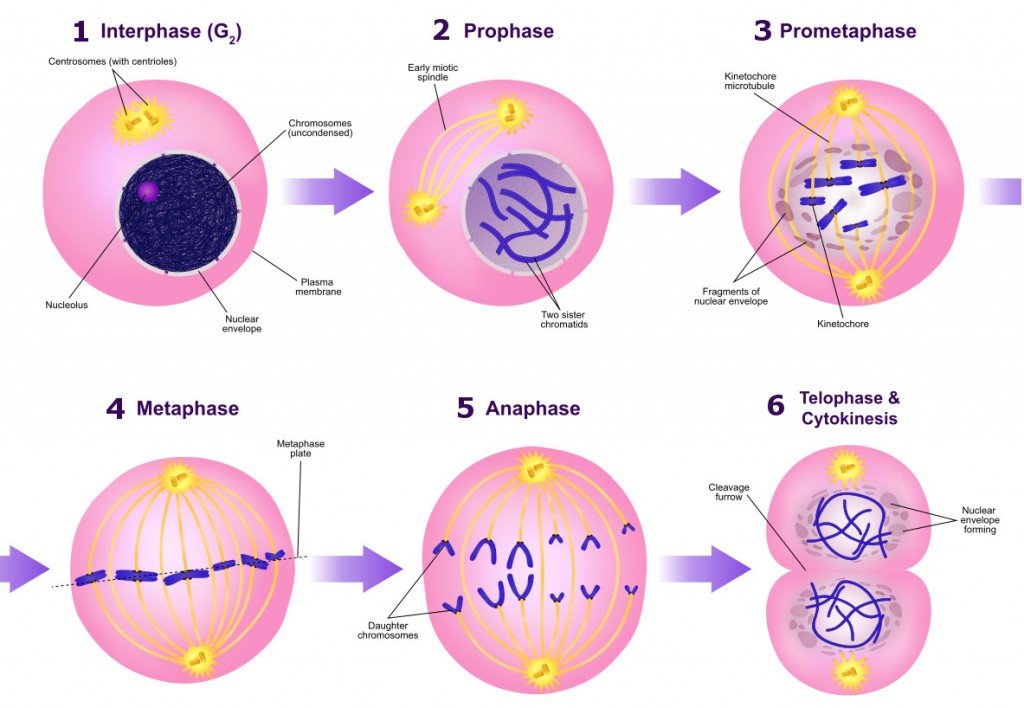
In Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G1, S, and G2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. This shuffling process is known as recombination or "crossing over" and occurs while the chromome pairs are lined up in Metaphase I. During this stage the chromosomes condense once again, the nuclear membrane. Each sibling is 50% mom and 50% dad, but which 50% of each can vary in the siblings. The next phase of meiosis is called Meiosis II. But this happens independently for each trait, so just because you got your dad's brown eyes doesn't mean you'll get his blond hair too. Each sperm and egg will end up with either B or b from mom and either B or b from dad. This leads to four possibilities: You could get B from mom and B from dad, or B from mom and b from dad, or b from mom and B from dad, or b from mom and b from dad. Imagine, for example, that eye color was controlled by a single gene, and that mom could have B, the allele for brown eyes or b, the allele for blue eyes, and dad could also have B or b.

But each non-identical-twin child of these parents ends up with a different combination. You ended up with half of mom's paired genes and half of dad's paired genes. Your parents each have at least one pair of alleles (versions of a gene) for every trait (and many pairs of alleles for each polygenic trait).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
